
It has actually been over 20 years because the discovery of dark energy.
Researchers have actually for that reason had more than 20 years to translate the tricks of this undetectable compound that seems pulling deep space apart. They still understand close to absolutely nothing about it. Dark energy, in reality, might not even be a compound. It might be a force or perhaps an intrinsic residential or commercial property of area itself.
The basic design of cosmology– our leading theory of cosmic advancement– does recommend dark energy is unwavering throughout the universe and throughout time, making it a basic residential or commercial property of area. If continuous, the mystical dark energy that comprises a massive 70 percent of deep space would press away all stars and galaxies. The most significant study of the universe's cosmic history might show that dark energy, likewise understood as a theoretical “anti-gravity” force, might progress with time rather than stay consistent, hinting at a less lonesome future for locals of the universe.
Related: 25 years after its discovery, dark energy stays frustratingly evasive
If this early outcome accepts future observations, cosmologists might need to, at least, check out organized unpredictabilities in the dominating Lambda CDM (LCDM) design, a mathematical design of deep space in which lambda represents dark energy. They might likewise require to begin sorting through lots of other designs of our universe to discover the real best fit. Still, the proof is tentative– it does not reach what's called the “5-sigma limit,” which identifies whether a signal can be commemorated as a main discovery. Continually emerging analyses about dark energy's advancement might alter with more information set up to come within the next couple of years.
“If this holds true, this simply turns cosmology upside down,” stated Dillon Brout of Boston University, who determines the velocity of deep space with supernovas. Such a discovery would be a “paradigm shift in our thinking about what our finest understanding of our universe is.”
Streetlights of deep space
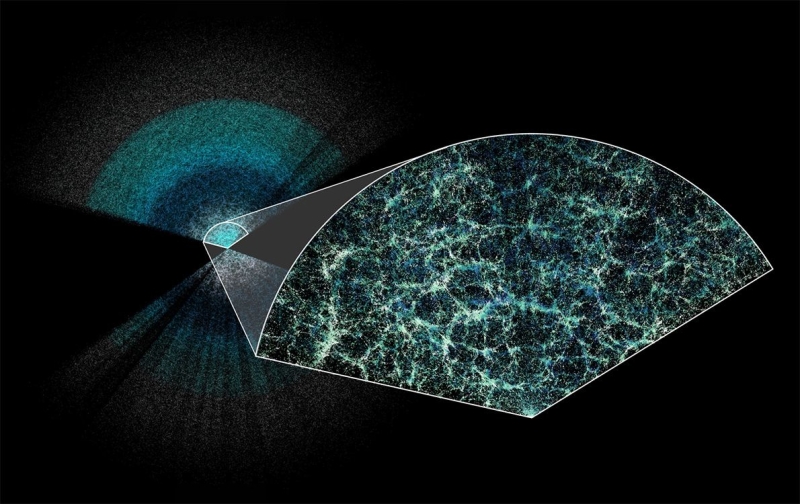
Perched atop the Nicholas U. Mayall 4-meter telescope at Arizona's Kitt Peak National Observatory, the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument, or DESI, determines positions of a million galaxies every month. Through these observations, cosmologists can determine deep space's growth rate as it increased over the previous 11 billion years. These far galaxies, which can be compared to the “streetlights of deep space,” are hence assisting cosmologists study the universe-permeating enigma of dark energy.
Breaking area news, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and more!
And, on Thursday (April 4), the DESI partnership shared the largest-ever 3D map of deep space. It consists of high-precision measurements of the universe's growth rate over the previous 11 billion years. In its very first year of operations alone, DESI has actually shown to be two times as effective at determining the growth history of the early universe as its predecessor, the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, which took more than a years to develop a comparable 3D map.
